The global pervasiveness of racism and segregation in the 1920s and 1930s
During the 1920s and 1930s, there were discriminatory policies in different parts of the world. These were mostly in European countries like Britain and European colonies like South Africa. These discriminatory policies were mostly on basis of Race, and were often in favour of white people’s interests. Black and white people were not allowed contact in different social domains. For instance in schools, white people had well-resourced schools with better facilities, while Black people had inadequate facilities like overcrowded schools with poor teaching and learning resources.
Segregation after formation of the Union
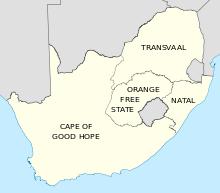 A map of the four provinces of the Union of South Africa Image source
A map of the four provinces of the Union of South Africa Image source
By 1910, South Africa (then Union of South Africa) was ruled by White people (descendants of white European settlers). This government was exclusively for white people. They were the only ones who participated in it, the only ones allowed to vote.
Under their leadership segregation laws were predominant and highly active. These segregation laws were implemented in spaces such as the work place. In the job market white people were given first priority, they were given upper position and paid higher salaries even if they had the same qualifications, experience and capabilities as Black people. Black people worked under poor and unsafe conditions and were denied the rights to join or form trade unions. In the army only white people could serve main roles like being a soldier, Black people were given supporting roles such as cooking and cleaning. Other segregation laws and policies included the Native Land Act of 1913 and the Pass laws.
National Party victory 1948
 National Party’s Logo. Image source
National Party’s Logo. Image source
The National Party’s victory in the 1948 elections can be linked with the dismantlement of segregation in South Africa during the Second World War. This was because of the growth in industries, where black people were in demand for labour in industries. Black people filled the positions that were left empty by the whites. White people could not fill these positions because they were few in numbers and most white people already occupied better jobs rather than physical manual labour. Large numbers of black people then moved to the cities to fill these vacancies and soon Blacks became the majority of labour in cities.
Black people were then given pieces of land outside cities to occupy. These pieces of lands were known as ghettos. The ghettos were often not too far from the cities, so Black people could get to work in the cities easy.
In the same year, 1948, when the National Party came to power, apartheid started. Apartheid resulted from white people’s frustrations and their dissatisfactions by the then overwhelming presence of Black people in cities. The large numbers of Black people in cities threatened white people’s power. To whites, it seemed like Black people would be difficult to control in cities than in Homelands. For Whites, apartheid would then re-affirm white superiority and would keep that Black people under their control.
Overcoming Apartheid - the nature of internal resistance to Apartheid before 1960
Internal resistance against apartheid began in the 1950s. This was when anti-apartheid groups rejected the apartheid system. They adopted a programme called the “programme of action”, which encompassed other internal resistance programmes such as:
- The Defiance campaign
- The African National congress
- The Freedom Charter
- The women Resistance movement
- Sharpeville Massacre
- Rivonia Trial
Also see: http://www.sahistory.org.za/topic/popular-struggles-early-years-apartheid-1948-1960
Review - ‘Apartheid’ becomes an international word; putting South Africa within a broader world context in relation to the uniqueness of Apartheid
 A Poster of sanctions against apartheid Image source
A Poster of sanctions against apartheid Image source
Under the apartheid system, the South African profile in terms of foreign relations did not look good. Many countries began ending their relationship with South Africa. As a result, South Africa became relatively isolated. Most countries in the world did not approve of the apartheid system in South Africa. This was because most countries and most people became more aware of human rights and learnt from past experiences of discriminations like the Holocaust .
See: http://www.sahistory.org.za/dated-event/european-community-lifts-sanctions-against-sa
See: http://www.sahistory.org.za/dated-event/un-lifts-mandatory-sanctions-against-sa
In 1946, the United Nations expressed its concerns about South Africa’s discriminatory policies, particularly how South Africa handled the issues of South African Indians, which caused tensions between South Africa and India.
In 1952, after the Defiance Campaign, the United Nations appointed a task team to monitor the progress of the apartheid system in South Africa. Possibly the UN was a bit lenient with South Africa regarding apartheid. Many countries in the UN felt that apartheid was South Africa’s internal issue, and was quite outside from UN issues.
However the UN became hard on South Africa regarding administration of South West Africa (now Namibia). This was because South Africa had refused grant South West Africa independence to Germany as it was stated on the Treaty of Versailles. The NP treated SWA as the fifth province of South Africa and spread apartheid in the country too.
In 1960 Liberia and Ethiopia called for the International Court of Justice to take legal actions against South Africa’s control of SWA. These two countries realised that apartheid was also expanding to other regions of in south west Africa.
In November 1960, a lawsuit, which would last for six years, was given to South Africa for poor administration of SWA. The International Court of Justice ruled that announced that Ethiopia and Liberia had no right to intervene in South Africa’s internal issues. No further rulings were made by the court regarding South Africa’s legitimacy over the administration of SWA. South Africa then continued to administer SA until its independence in 1988.
After showing signs of improvement on racial discrimination, such as negotiations about ending the apartheid system, the release of Political prisoners like the release of Nelson Mandela in 1990, and the African National Congress’ lift on the armed struggle, South Africa finally earned its freedom in 1994, and soon formed the
The global pervasiveness of racism and segregation in the 1920s and 1930s
During the 1920s and 1930s, there were discriminatory policies in different parts of the world. These were mostly in European countries like Britain and European colonies like South Africa. These discriminatory policies were mostly on basis of Race, and were often in favour of white people’s interests. Black and white people were not allowed contact in different social domains. For instance in schools, white people had well-resourced schools with better facilities, while Black people had inadequate facilities like overcrowded schools with poor teaching and learning resources.
Segregation after formation of the Union
 A map of the four provinces of the Union of South Africa Image source
A map of the four provinces of the Union of South Africa Image source
By 1910, South Africa (then Union of South Africa) was ruled by White people (descendants of white European settlers). This government was exclusively for white people. They were the only ones who participated in it, the only ones allowed to vote.
Under their leadership segregation laws were predominant and highly active. These segregation laws were implemented in spaces such as the work place. In the job market white people were given first priority, they were given upper position and paid higher salaries even if they had the same qualifications, experience and capabilities as Black people. Black people worked under poor and unsafe conditions and were denied the rights to join or form trade unions. In the army only white people could serve main roles like being a soldier, Black people were given supporting roles such as cooking and cleaning. Other segregation laws and policies included the Native Land Act of 1913 and the Pass laws.
National Party victory 1948
 National Party’s Logo. Image source
National Party’s Logo. Image source
The National Party’s victory in the 1948 elections can be linked with the dismantlement of segregation in South Africa during the Second World War. This was because of the growth in industries, where black people were in demand for labour in industries. Black people filled the positions that were left empty by the whites. White people could not fill these positions because they were few in numbers and most white people already occupied better jobs rather than physical manual labour. Large numbers of black people then moved to the cities to fill these vacancies and soon Blacks became the majority of labour in cities.
Black people were then given pieces of land outside cities to occupy. These pieces of lands were known as ghettos. The ghettos were often not too far from the cities, so Black people could get to work in the cities easy.
In the same year, 1948, when the National Party came to power, apartheid started. Apartheid resulted from white people’s frustrations and their dissatisfactions by the then overwhelming presence of Black people in cities. The large numbers of Black people in cities threatened white people’s power. To whites, it seemed like Black people would be difficult to control in cities than in Homelands. For Whites, apartheid would then re-affirm white superiority and would keep that Black people under their control.
Overcoming Apartheid - the nature of internal resistance to Apartheid before 1960
Internal resistance against apartheid began in the 1950s. This was when anti-apartheid groups rejected the apartheid system. They adopted a programme called the “programme of action”, which encompassed other internal resistance programmes such as:
- The Defiance campaign
- The African National congress
- The Freedom Charter
- The women Resistance movement
- Sharpeville Massacre
- Rivonia Trial
Also see: http://www.sahistory.org.za/topic/popular-struggles-early-years-apartheid-1948-1960
Review - ‘Apartheid’ becomes an international word; putting South Africa within a broader world context in relation to the uniqueness of Apartheid
 A Poster of sanctions against apartheid Image source
A Poster of sanctions against apartheid Image source
Under the apartheid system, the South African profile in terms of foreign relations did not look good. Many countries began ending their relationship with South Africa. As a result, South Africa became relatively isolated. Most countries in the world did not approve of the apartheid system in South Africa. This was because most countries and most people became more aware of human rights and learnt from past experiences of discriminations like the Holocaust .
See: http://www.sahistory.org.za/dated-event/european-community-lifts-sanctions-against-sa
See: http://www.sahistory.org.za/dated-event/un-lifts-mandatory-sanctions-against-sa
In 1946, the United Nations expressed its concerns about South Africa’s discriminatory policies, particularly how South Africa handled the issues of South African Indians, which caused tensions between South Africa and India.
In 1952, after the Defiance Campaign, the United Nations appointed a task team to monitor the progress of the apartheid system in South Africa. Possibly the UN was a bit lenient with South Africa regarding apartheid. Many countries in the UN felt that apartheid was South Africa’s internal issue, and was quite outside from UN issues.
However the UN became hard on South Africa regarding administration of South West Africa (now Namibia). This was because South Africa had refused grant South West Africa independence to Germany as it was stated on the Treaty of Versailles. The NP treated SWA as the fifth province of South Africa and spread apartheid in the country too.
In 1960 Liberia and Ethiopia called for the International Court of Justice to take legal actions against South Africa’s control of SWA. These two countries realised that apartheid was also expanding to other regions of in south west Africa.
In November 1960, a lawsuit, which would last for six years, was given to South Africa for poor administration of SWA. The International Court of Justice ruled that announced that Ethiopia and Liberia had no right to intervene in South Africa’s internal issues. No further rulings were made by the court regarding South Africa’s legitimacy over the administration of SWA. South Africa then continued to administer SA until its independence in 1988.
After showing signs of improvement on racial discrimination, such as negotiations about ending the apartheid system, the release of Political prisoners like the release of Nelson Mandela in 1990, and the African National Congress’ lift on the armed struggle, South Africa finally earned its freedom in 1994, and soon formed the Truth And Reconciliation Commission.